The path of designing digital transformation maturity model

How Market Research Empowers Companies
December 26, 2023
Strategic Exploration of Innovation Maturity: Innotech’s Systematic Framework
January 6, 2024
In the previous section, we explored the distinction between the general digital transformation maturity model and the industrial digital transformation maturity model. The general model provides a broad and adaptable framework applicable across diverse industries, guiding organizations through the stages of digital transformation by addressing universal principles such as strategy alignment, technological integration, and cultural shifts. On the other hand, the industrial digital transformation maturity model is specifically tailored for sectors like manufacturing, energy, and logistics. It hones in on industry-specific challenges and opportunities, emphasizing elements like smart manufacturing, IoT implementation, and supply chain optimization. This focused approach enables industrial organizations to navigate the intricacies of their sector, promoting digital maturity that is finely tuned to their unique operational needs and positioning them for enhanced efficiency and competitiveness within their industry.
Designing a digital transformation maturity model involves a systematic and strategic process to provide organizations with a structured framework for assessing and advancing their digital capabilities. The following outlines a path for designing a digital transformation maturity model:
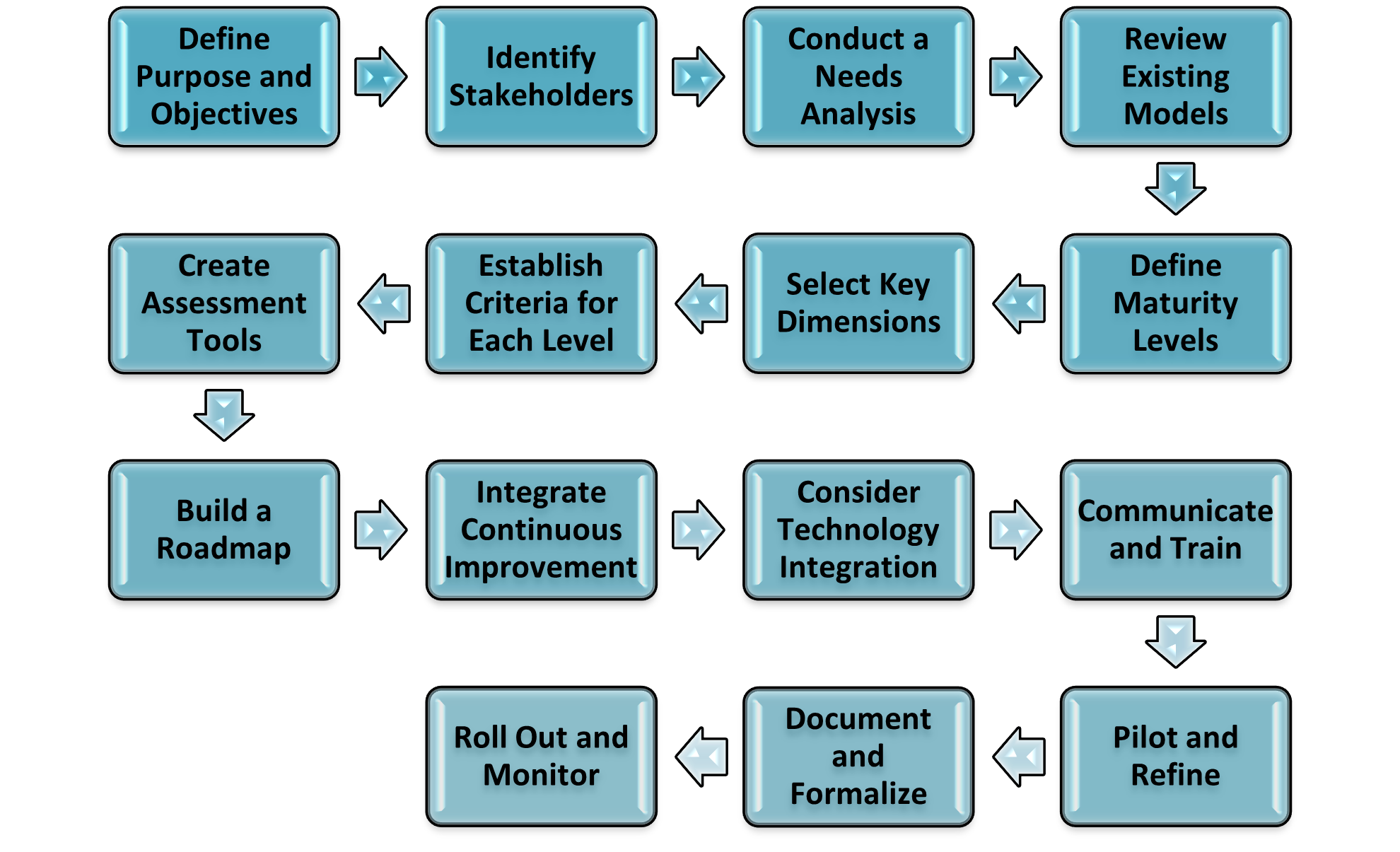
1. Define Purpose and Objectives:
- Clearly articulate the purpose of the maturity model. Understand whether it’s for self-assessment, benchmarking, or guiding digital transformation efforts.
- Define the specific objectives you aim to achieve with the maturity model.
2. Identify Stakeholders:
- Identify and involve key stakeholders in the design process, including executives, department heads, IT leaders, and other relevant personnel.
- Understand their perspectives, expectations, and the specific challenges they face.
3. Conduct a Needs Analysis:
- Analyze the unique needs and context of your organization. Consider industry-specific requirements, regulatory constraints, and organizational goals.
- Identify the critical areas of digital transformation that need to be assessed.
4. Review Existing Models:
- Research and review existing digital transformation maturity models. Understand their structures, key dimensions, and criteria.
- Identify elements that align with your organization’s goals and context.
5. Define Maturity Levels:
- Determine the maturity levels that will be part of the model.
- Clearly define the characteristics of each level in terms of processes, technologies, culture, and organizational capabilities.
6. Select Key Dimensions:
- Identify the key dimensions or domains that contribute to digital maturity. Examples include strategy, leadership, culture, technology, data, and processes.
- Ensure that the chosen dimensions align with the organization’s strategic goals.
7. Establish Criteria for Each Level:
- Define specific criteria for each maturity level within each dimension. These criteria should be measurable, observable, and indicative of the organization’s maturity in that area.
8. Create Assessment Tools:
- Develop assessment tools or surveys that organizations can use to evaluate their maturity levels. Consider a mix of self-assessment, interviews, and objective metrics.
- Ensure that the assessment tools align with the defined criteria for each dimension and maturity level.
9. Build a Roadmap:
- Develop a roadmap that outlines the steps organizations can take to progress from one maturity level to the next.
- Provide guidance on the specific actions, investments, and changes needed to advance digital maturity.
10. Integrate Continuous Improvement:
- Incorporate mechanisms for continuous improvement. Allow organizations to revisit their assessments periodically and update their digital transformation strategies accordingly.
- Consider feedback loops, learning mechanisms, and adaptability in the design to ensure ongoing relevance.

11. Consider Technology Integration:
- Explore the integration of technology solutions that can facilitate the assessment and monitoring process.
- Leverage digital tools for data collection, analysis, and visualization.
12. Communicate and Train:
- Develop a communication plan to introduce the maturity model to the organization. Ensure that all stakeholders understand its purpose, benefits, and how to use it.
- Provide training and support resources to guide users through the assessment process.
13. Pilot and Refine:
- Pilot the maturity model in a specific department or business unit before rolling it out organization-wide.
- Collect feedback from users and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. Refine the model based on real-world implementation experiences.
14. Document and Formalize:
- Document the maturity model, including its components, criteria, and assessment processes.
- Establish formal processes for governance, updates, and maintenance.
15. Roll Out and Monitor:
- Roll out the maturity model organization-wide. Monitor its adoption and impact.
- Establish regular reviews to ensure the model remains aligned with organizational goals and industry trends.
Remember that the design process is iterative, and adjustments may be necessary based on the feedback and evolving needs of the organization. Regularly update the maturity model to ensure it remains a valuable tool for guiding digital transformation efforts.